Experimental Production of Excess Brain Correlation across the Atlantic Ocean & Other Important Results
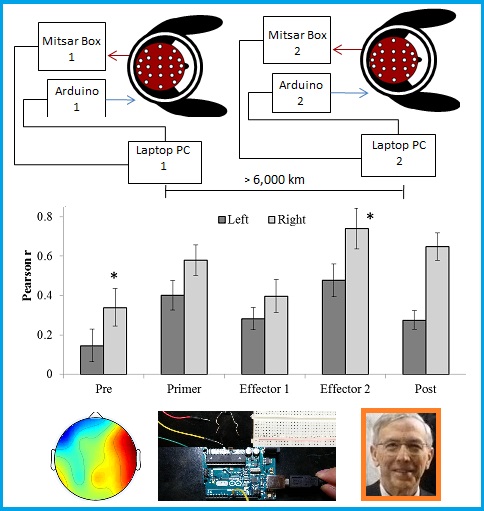
Experimental Production of Excess Correlation across the Atlantic Ocean of Right Hemispheric Theta-Gamma Power between Subject Pairs Sharing Circumcerebral Rotating Magnetic Fields (Part I) by Mandy A. Scott, Nicolas Rouleau, Brendan S. Lehman, Lucas W. E. Tessaro, Lyndon M. Juden-Kelly, Kevin S. Saroka, Michael A. Persinger
There have been multiple historical and cross-cultural reports of excess correlation of specific experiences between individuals separated by thousands of kilometers. Recently there have been experimental demonstrations of excess correlations between measurable cerebral events for small percentages of test subjects. More reliable effects can be elicited when electromagnetic fields and photons are involved. In this experiment completed during the summer of 2015, 5 pairs of volunteers separated by more than 6,000 km wore identical cerebral toroids through which patterns of phase shifting, 30 nT magnetic fields that diminished the local magnetic field in both loci by 1-5 nT were exposed to the sequences that produced excess correlation in chemiluminescent reactions and shifts in pH. Compared to the various baselines and control procedures enhanced power between the right hemispheres of pairs of participants occurred during the interval documented to produce excess correlation. Specific analyses indicated diminished coherence within the theta band only within the right temporal lobes of the pairs. Sequential block analyses revealed that the paired brains’ responses to pulsed tones at 6.5 Hz occurred within the 30-40 Hz band over the caudal temporal lobes during the exposures to the effector field. Primary independent component analyses verified these patterns. During the 6.5 Hz tones there was a peak in the spectral power density (SPD) at that frequency over the right temporal lobe of the person listening but a trough in (SPD) over this region for the person who was not. Even subjective experiences, as measured by the Profile of Mood States (POMS), indicated significantly increased excess correlation for scales by which increased anger and decreased vigour are inferred. This experiment, based upon physical principles, suggests there is a technology that can generate reliable excess correlation of brain activity (and potentially consciousness and specific experiences) between two people separated by thousands of kilometers. Part I of this two-part article includes: 1. Introduction; 2. Method; 3. Equipment; and 4. Results and Discussion. See http://jcer.com/index.php/jcj/article/view/493
Experimental Production of Excess Correlation across the Atlantic Ocean of Right Hemispheric Theta-Gamma Power between Subject Pairs Sharing Circumcerebral Rotating Magnetic Fields (Part II) by Mandy A. Scott, Nicolas Rouleau, Brendan S. Lehman, Lucas W. E. Tessaro, Lyndon M. Juden-Kelly, Kevin S. Saroka, Michael A. Persinger
There have been multiple historical and cross-cultural reports of excess correlation of specific experiences between individuals separated by thousands of kilometers. Recently there have been experimental demonstrations of excess correlations between measurable cerebral events for small percentages of test subjects. More reliable effects can be elicited when electromagnetic fields and photons are involved. In this experiment completed during the summer of 2015, 5 pairs of volunteers separated by more than 6,000 km wore identical cerebral toroids through which patterns of phase shifting, 30 nT magnetic fields that diminished the local magnetic field in both loci by 1-5 nT were exposed to the sequences that produced excess correlation in chemiluminescent reactions and shifts in pH. Compared to the various baselines and control procedures enhanced power between the right hemispheres of pairs of participants occurred during the interval documented to produce excess correlation. Specific analyses indicated diminished coherence within the theta band only within the right temporal lobes of the pairs. Sequential block analyses revealed that the paired brains’ responses to pulsed tones at 6.5 Hz occurred within the 30-40 Hz band over the caudal temporal lobes during the exposures to the effector field. Primary independent component analyses verified these patterns. During the 6.5 Hz tones there was a peak in the spectral power density (SPD) at that frequency over the right temporal lobe of the person listening but a trough in (SPD) over this region for the person who was not. Even subjective experiences, as measured by the Profile of Mood States (POMS), indicated significantly increased excess correlation for scales by which increased anger and decreased vigour are inferred. This experiment, based upon physical principles, suggests there is a technology that can generate reliable excess correlation of brain activity (and potentially consciousness and specific experiences) between two people separated by thousands of kilometers. Part II of this two-part article includes: 4. Results and Discussion (continued); 5. General Discussion; Appendix A; and References. See http://jcer.com/index.php/jcj/article/view/487
On the Nature of & Relation between Form & Formlessness: Part 1: The Evolution of the Formless into Form while Creating Lesser Form (2) by Steven E. Kaufman
In the first part of this work the evolution of the Formless into three different levels of Form is described. Also described in the first part of this work is the coming into existence of a different type of form, or lesser form, within each level of Form, as each level of Form comes into being through the progressive flow of the Formless in relation to Itself. Further, the three different types of lesser forms that come into existence within the Formless, as the Formless, through iterative and progressive relation to Itself, evolves into different levels of Form, are each shown to correspond to one of the three different types of experiences or experiential realities of which we are able to be aware or conscious. Specifically, the lesser form that comes into existence within the first level of Form, as the first level of Form comes into being, will be shown to correspond to what we apprehend as emotional experience or emotional reality. Next, the lesser form that comes into existence within the second level of Form, as the second level of Form comes into being, will be shown to correspond to what we apprehend as mental experience or mental reality. And finally, the lesser form that comes into existence within the third level of Form will be shown to correspond to what we apprehend as physical experience or physical reality. This second article of Part 1 contains the following sections: Why math and language work; The third level of form; The actual difference between animate and inanimate objects; The animation of second level Forms; The propagation of animate Form, i.e., the reproduction of life; & The apprehension of mental and physical reality as Beingness flows through Form. See http://jcer.com/index.php/jcj/article/view/494
Spectral Power Densities of the Fundamental Schumann Resonance Are Enhanced in Microtubule Preparations Exposed to Temporally Patterned Weak Magnetic Fields: Implications for Entanglement by Blake T. Dotta, David A. E. Vares, Michael A. Persinger
Preparations of microtubules (MT) from mouse melanoma cells emitted predictable photon counts when sampled 50 times per s (every 20 ms) that depended upon the numbers of these preparations. Counterbalanced serial 4 min exposures of the same MT to different temporally patterned magnetic fields with intensities between 3 and 10 μT did not alter the absolute photon emissions but shifted their spectral power densities (SPD). Compared to baseline (no field) 4 min periods there were conspicuous increases of power within the 7.7 to 7.8 Hz band during the 4 min exposures to patterned magnetic fields that facilitate long-term potentiation in neurons but not during exposures to a pattern associated with analgesia. A priori predictions of the shift in frequency (Δf) based upon the median mass of tubulin dimers, known numbers of unit charges per dimer, and the strength of the applied fields predicted a range between 0.11 and 0.14 Hz. SPD demonstrated two peaks at 7.74 Hz and 7.87 Hz or a Δf=0.13 Hz. The results indicate only 4 min exposures of microtubule preparations to specifically physiologically patterned magnetic fields associated with memory consolidation enhance the power of the numbers of photon emissions in a frequency band that is very similar to the fundamental Schumann Resonance. See http://jcer.com/index.php/jcj/article/view/496
Demonstration of Excess Correlation in Non-Local Random Number Generators Sharing Circular, Changing Angular Velocity Magnetic Fields by Lyndon M. Juden-Kelly, Blake T. Dotta, David A. E. Vares, Michael A. Persinger
To test if temporally-coupled diametric shifts in parity could be demonstrated for non-local distances between “random” events generated by electron tunnelling-based circuits, two REG (Random Event Generators) were each exposed within a circular array of solenoids separated by 10 m. Each circular array generated a patterned rotating magnetic field that has previously produced transient excess correlation and entanglement in photon reactions and alterations in pH in spring water. During a 30 min interval the REGs were exposed first to an accelerating group velocity embedded with a diminishing frequency/phase-modulated field (the primer) followed by a decelerating group velocity embedded with an increasing frequency/phase-modulated magnetic field (the effector). Only after exposures for about 4 min to the second (effector) condition that is known to manifest the effects of entanglement did the random numbers deviate significantly and by more than one standard deviation in an opposite direction to each other. The estimated increments of energy were between 10-21 and 10-20 J which is within the range of the energy derived from the universe’s total force per Planck’s voxel distributed over the distance of the hydrogen wavelength. These results indicate that excess correlation can be generated within “random”, quantum electronic processes whose spatial domains are similar to neuronal synapses at the macro-level by appropriate applications of weak, microTesla level, magnetic fields. See http://jcer.com/index.php/jcj/article/view/497
- Log in to post comments




Recent comments